
Welcome
Systematic, Comprehensive, In depth and Strategic Consulting
Global, Prediction, Precision, Prevention, Personalized, Population and Policy

Global, Prediction, Precision, Prevention, Personalized, Population and Policy

Post on July 24, 2023

Post on August 31, 2020
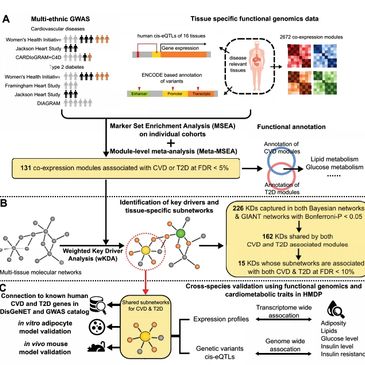
Design/Analysis/Interpretation/Translation

Design/Analysis/Interpretation/Translation

Design/Analysis/Interpretation/Translation

Design/Analysis/Interpretation/Translation

Design/Analysis/Interpretation/Translation

Data and Safety Monitoring

Design/Analysis/Interpretation/Translation

This is the first comprehensive and systematic human biomonitoring study that established population reference ranges for 30 (essential and/or toxic elements) in a Brazilian population group.

We analyzed diabetes-free participants from 10 cohorts in the NHLBI Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine (TOPMed) program to identify macronutrient GDIs across the genetic frequency spectrum associated with continuous glycemic traits in genetically and culturally diverse cohorts.

The study aimed to determine the predictive value of circulating sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels for coronary heart disease (CHD) risk in both men and women, by investigating the association between SHBG and incident CHD in 128,322 men and 135,103 women free of CHD at baseline in the UK Biobank cohort.

This systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled intervention trials emphasizes the significance of diverse micronutrient intake and balancing its benefits and risks in promoting and maintaining cardiovascular health across diverse populations.

We aimed to determine the association between prenatal exposure to the Chinese famine of 1959–1962 and risk of diabetes by applying age well-controlled strategies.

Demographic and clinical factors influence the metabolome. The discovery and validation of disease biomarkers are often challenged by potential confounding effects from such factors. To address this challenge, we investigated the magnitude of the correlation between serum and urine metabolites and demographic and clinical parameters in a well-characterized observational cohort of 444 post-menopausal women participating in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI)

The age of natural menopause (ANM) was observationally associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and ovarian cancer and with a decreased risk of lung cancer, coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke, fracture, osteoporosis, and Alzheimer's disease in the Women’s Health Initiative and UK Biobank; however, to address potential confounding by overall markers of health, a genetic instrument variable was used in Mendelian randomization to examine the causal effect of ANM on these adverse outcomes.

Among women with prior BSO, in those aged 70 years or older, CEE led to adverse effects during the treatment period, whereas women randomly assigned to CEE before age 60 seemed to derive mortality benefit over the long term.

sex- and gender- differences for the fundamental roles of sex-hormones, SHBG, and their environmental disruptors in cardiometabolic health are therefore crucia

evaluating the association of plasma levels of testosterone, sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG), and estradiol with risk of type 2 diabetes.

Menopausal hormone therapy continues in clinical use but questions remain
regarding its risks and benefits for chronic disease prevention.

liquid meal replacements replacing 1-2 meals per day or all meals (TDR) may have cardiometabolic advantages over traditional weight loss diets in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes, with DNSFs potentially providing even greater benefits for glycemic control compared to standard formulas.

Despite significant advances in DNAm-based deconvolution, references at the population level are needed for clinical and research interpretation of these additional immune layers. Here we aim to provide some references for immune populations in a group of multi-ethnic post-menopausal American women.

We present a well-phenotyped, densely genotyped, multi-ancestry resource to study gene-drug interactions, uncover novel variation associated with response to common glucose-lowering medications and provide insight into mechanisms of action of type 2 diabetes-related variation.

We use WHI observational data for further insight into the chronic disease implications of adopting this type of low-fat dietary pattern.

We sought to investigate the potential association between a personal history of being born preterm and risk for type 2 diabetes in a racially and ethnically diverse population.

Increase in BMI in the US that occurred during the 80s may portend an increase in the incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with important public health consequences in future years.

Diet and/or exercise interventions led to a significant decrease in the incidence of diabetes over a 6-year period among those with IGT.

Good protein sources are important for#diabetes#body weight or perhaps even #planetary health

A prospective study of dietary glycemic load, carbohydrate intake, and risk of coronary heart disease in US women

Relation between a diet with a high glycemic load and plasma concentrations of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in middle-aged women

First prospective study comprehensively assess circulation sex steroids, sex hormones binding globulin, and diabetes risk

First prospective study identifying SHBG gene, SHBG proteina causal predictor for type 2 diabetes in white men and white women

In this prospective study of women in the USA, we confirmed that LBW was significantly associated with increased type 2 diabetes risk later in life. We found that insulin resistance mediated a considerable amount of the total effect on type 2 diabetes risk due to LBW. This effect was further mediated by low SHBG concentration, elevated blood E-selectin level, and increased systolic blood pressure.s.
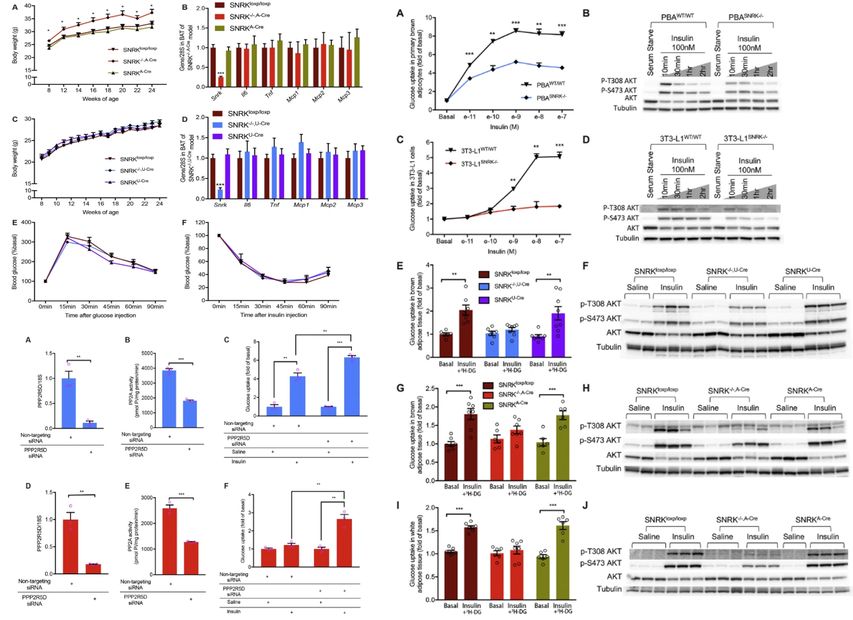
The role of SNRK in insulin signaling in white (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT)
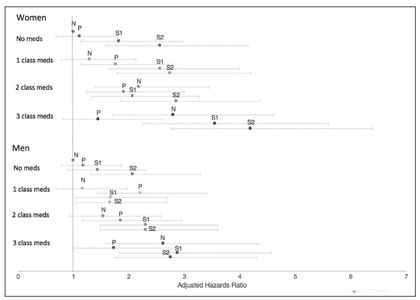
Sex Differences in Hypertension and Stroke Risk in the REGARDS Study A Longitudinal Cohort Study
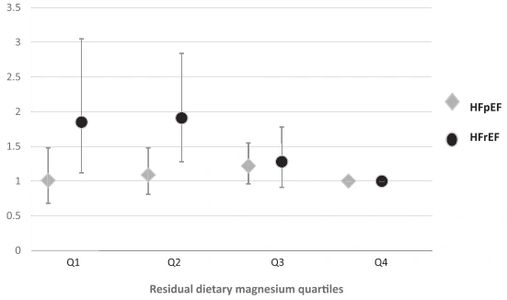
The association between magnesium intake and heart failure in a multiracial cohort of women
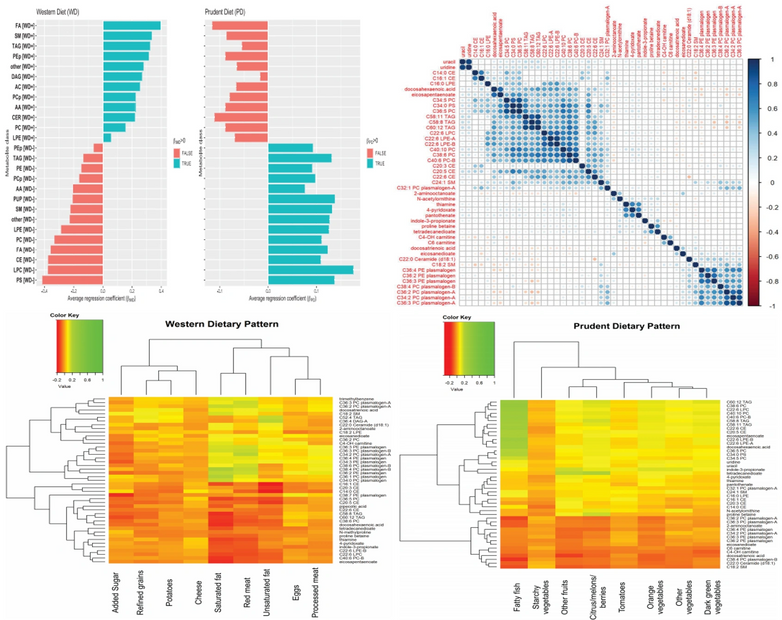
Assess the association of 2 derived dietary pattern scores with serum metabolites and identify metabolic pathways associated with the metabolites

There was no association between Lp(a) level and risk of 6 AAA in the Women’s Health Initiative

Provide a comprehensive and most up-to-date evidence-based map that systematically quantifies the impact of micronutrients on CVD outcomes.